Introduction
Refactoring codebases is a common task among software developers. Tests should give a certain confidence to implement changes without actually destroying critical parts. However, sometimes a refactoring process takes time. To be able to still release a pattern can be applied: Branch By Abstraction.
Martin Fowler describes it in his blog as a:
technique for making a large-scale change to a software system in a gradual way that allows you to release the system regularly while the change is still in progress.
Usage
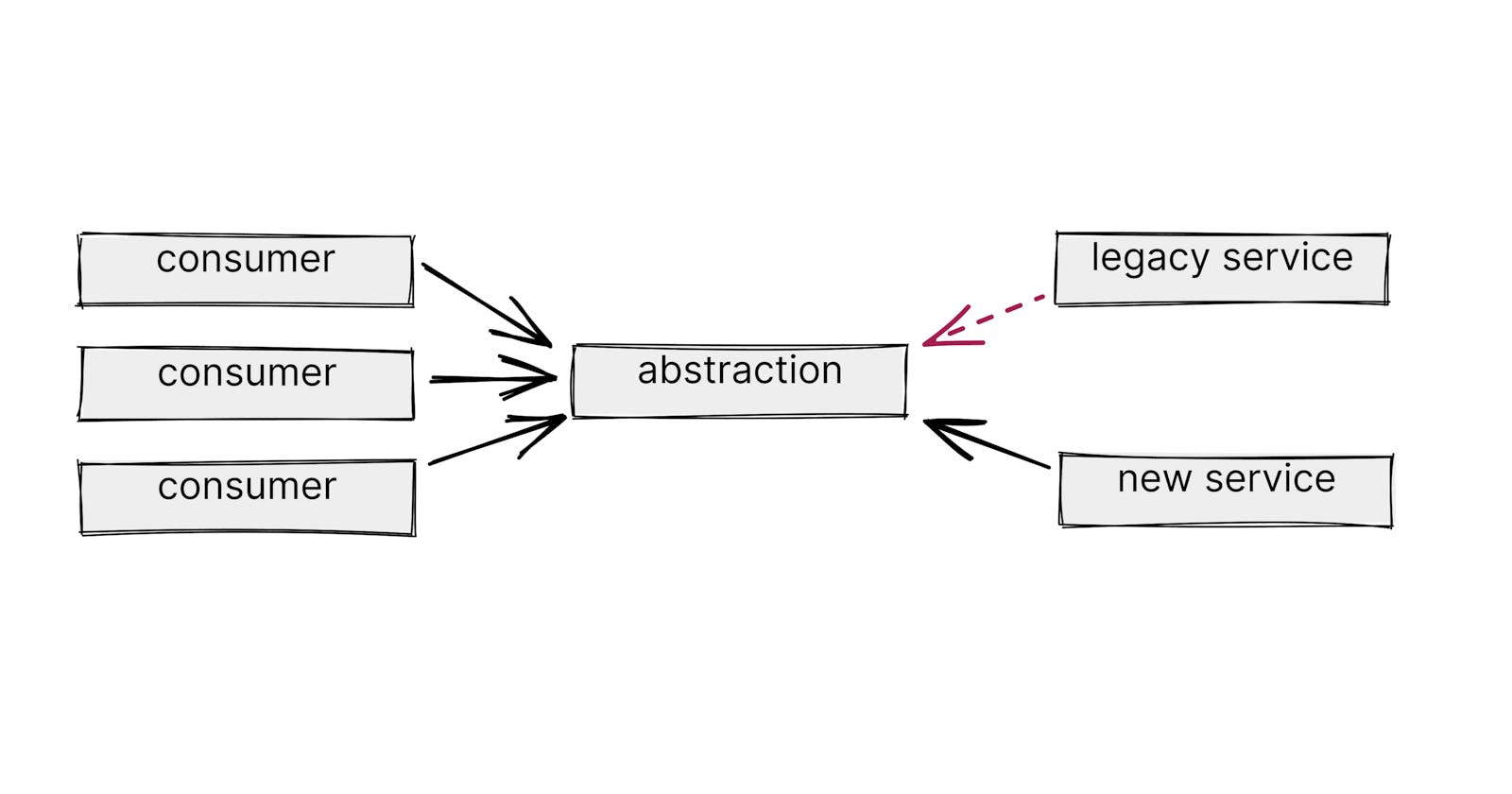
Let us assume the following use case: We have a legacy application and it contains a service that frustrates the dev team as its implementation is not easy to follow and therefore needs some refactoring.
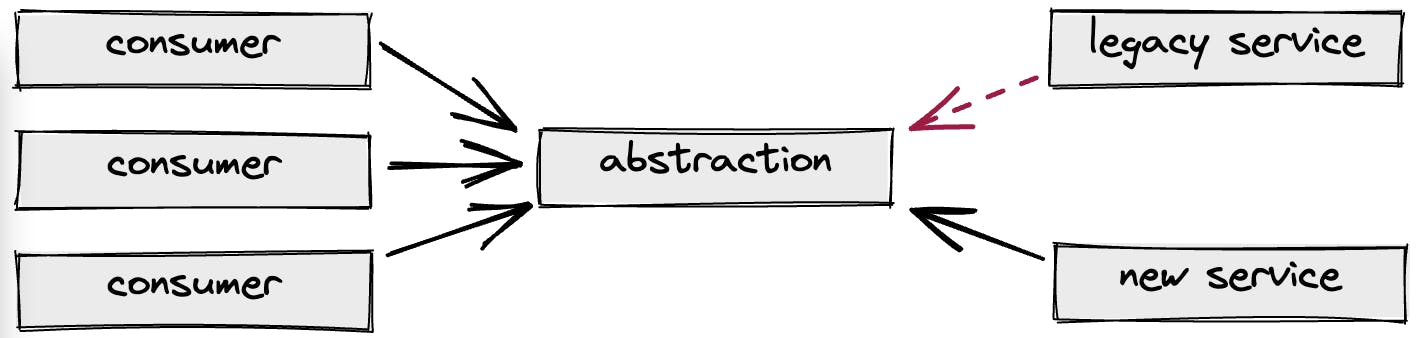
- Introduce an abstraction around the legacy service e.g. by introducing an interface. This abstraction should obviously not break the build
- Use the new abstraction
- Write a second implementation of the legacy service e.g. the new service for the given abstraction
- Remove the legacy service and switch to the new implementation
- Remove the abstraction
The whole process is enhanced by adding feature toggles. Step 2 should introduce such toggles like "off", "false", and "legacy" ..., while Step 3 switches this toggle to the new service.
Branch By Abstraction is often used withintrunk-based development
Example with NestJS
Give the following project structure:
├── app.controller.ts
├── app.module.ts
├── legacy.service.ts
├── main.ts
import { Injectable } from '@nestjs/common'
@Injectable()
export class LegacyService {
reverseInput(input: string): string {
const result = []
for (const i of input) {
result.unshift(i)
}
return result.join('')
}
}
import { Controller, Get } from '@nestjs/common'
import { LegacyService } from './legacy.service'
@Controller()
export class AppController {
constructor(private readonly legacyService: LegacyService) {}
@Get()
getReverseInput(): string {
return this.legacyService.reverseInput('test')
}
}
Introduce an abstraction
nest generate interface abstraction
export interface Abstraction {
reverseInput(input: string): string
}
Use the abstraction interface
...
export class LegacyService implements Abstraction
...
Write a second implementation of the service for the given abstraction
import { Injectable } from '@nestjs/common'
import { Abstraction } from './abstraction.interface'
@Injectable()
export class NewService implements Abstraction {
reverseInput(input: string): string {
return input.split('').reverse().join('')
}
}
Remove the legacy service e.g. switch to the new service
import { Controller, Get } from '@nestjs/common'
import { NewService } from './new.service'
@Controller()
export class AppController {
constructor(private readonly newService: NewService) {}
@Get()
getReverseInput(): string {
return this.newService.reverseInput('test')
}
}